Electrical Insulator
Electrical Insulator
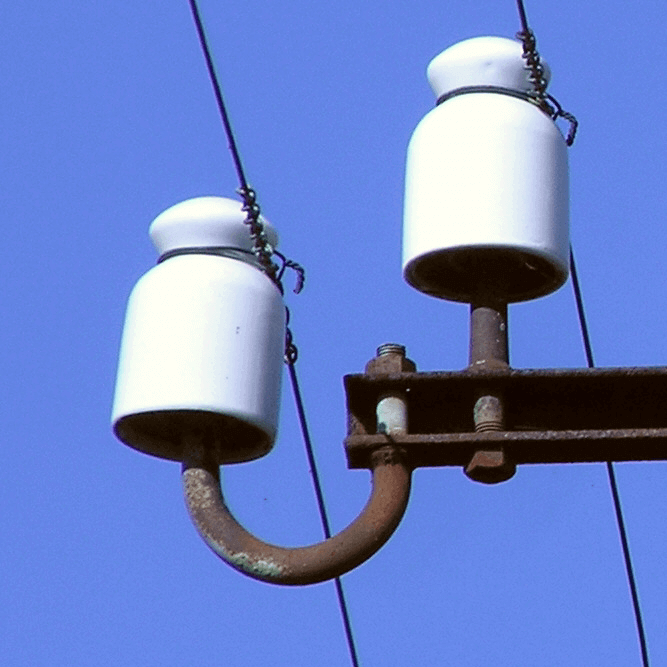
An electrical insulator prevents the unwanted flow of current by providing high resistance between conductive parts. Essential in power transmission systems, these materials ensure isolation, enhance safety, and protect equipment from arcing and short circuits.
Understanding How an Electrical Insulator Works

An electrical insulator is a material that restricts the flow of electric current, ensuring that electric charge does not easily pass through it. They are essential components in power systems, as they help protect equipment, structures, and people from electric shocks and short circuits. A high-quality electrical insulator possesses high resistivity, which means it can withstand high voltages without allowing current to flow unimpeded.
High Voltage Transmission Uses
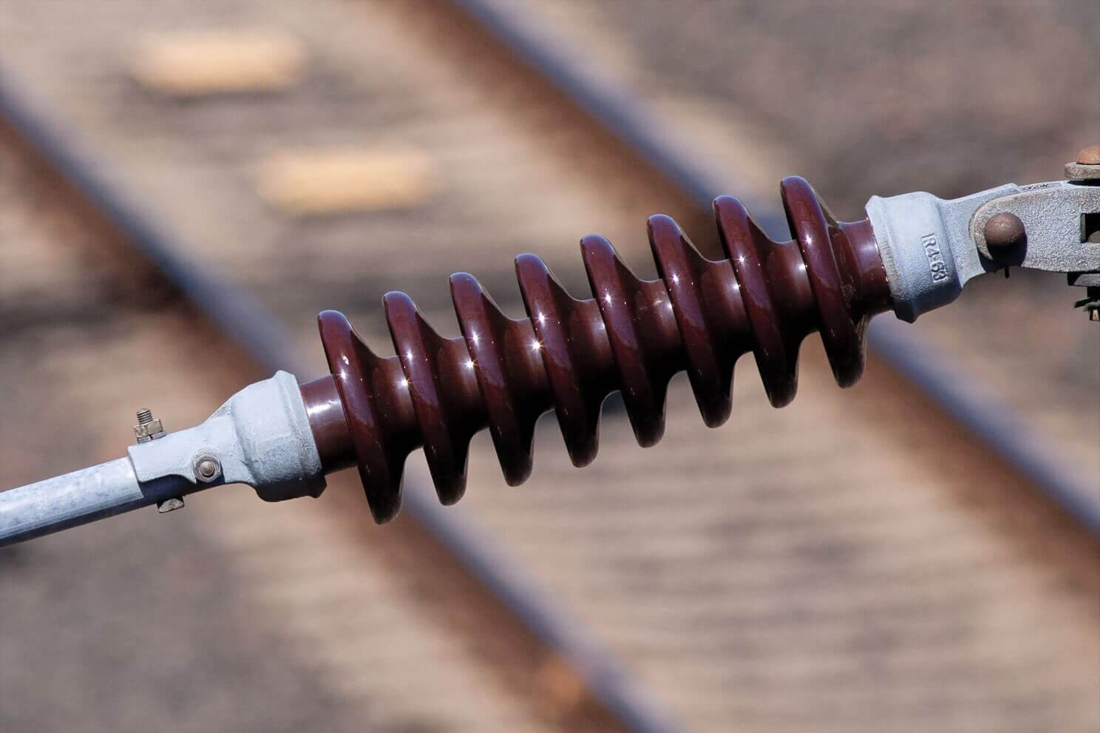
Electric utilities sometimes use polymer composite materials for certain types of insulators. These typically consist of a central rod of fibre-reinforced plastic and an outer weather shield made of silicone rubber or ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber. Composite non-conductive materials are more cost-effective and lightweight, exhibiting exceptional hydrophobic properties. This combination makes them ideal for use in areas with high pollution levels. However, these materials have not demonstrated the same long-term service life as their glass and porcelain counterparts.
Different Materials
Dielectric materials are a crucial component of any electrical insulator. They function by inhibiting the electric field within their structure, preventing the flow of a charge. A dielectric material's insulating properties are primarily determined by its dielectric constant, which measures its ability to store energy without conducting it.
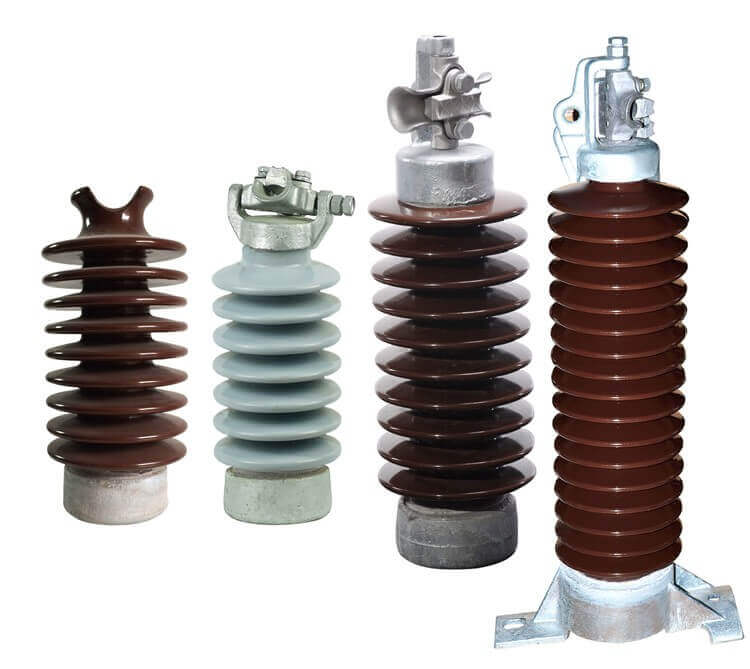
Ceramic ones, such as porcelain, have been used for many years due to their excellent insulating properties, mechanical strength, and resistance to high temperatures. They are typically used in high-voltage applications, including power transmission and distribution systems. However, they can be heavy and brittle, which reduces durability and increases maintenance costs.
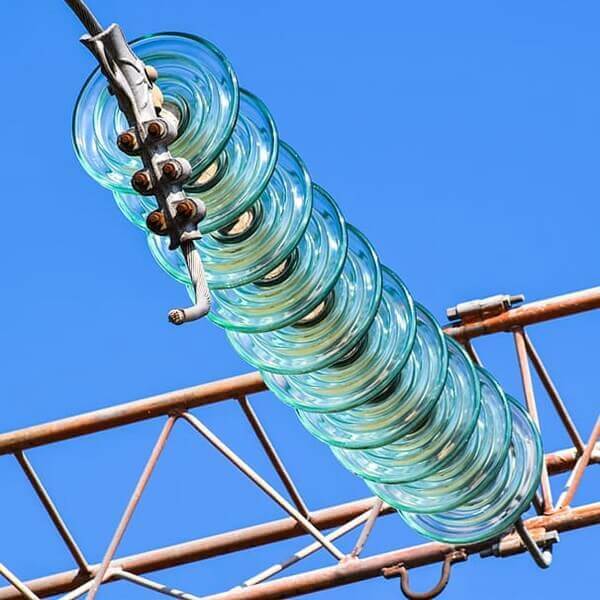
Materials such as glass paper, on the other hand, offer excellent transparency and a smooth surface that helps prevent dirt accumulation. They also have high dielectric strength, meaning they can withstand high voltage without breaking down. However, like ceramic ones, they are fragile and prone to breakage
Polymer insulators are a recent innovation made from silicone rubber or epoxy resins. They are lightweight, durable, and have good insulating properties. Additionally, polymer devices exhibit increased resistance to environmental factors, including UV radiation and pollution. However, their long-term performance still needs to be studied, and they may be more expensive than traditional ceramic or glass insulators.
Performance is affected by its resistance and breakdown voltage. Resistance measures a material's ability to prevent the flow of electric current. A higher resistance means that the insulating device is more effective at blocking the flow of electricity. On the other hand, the breakdown voltage is the maximum voltage an insulator can withstand before it fails and allows electric current to flow through it. Therefore, a higher breakdown voltage indicates better insulating capabilities.
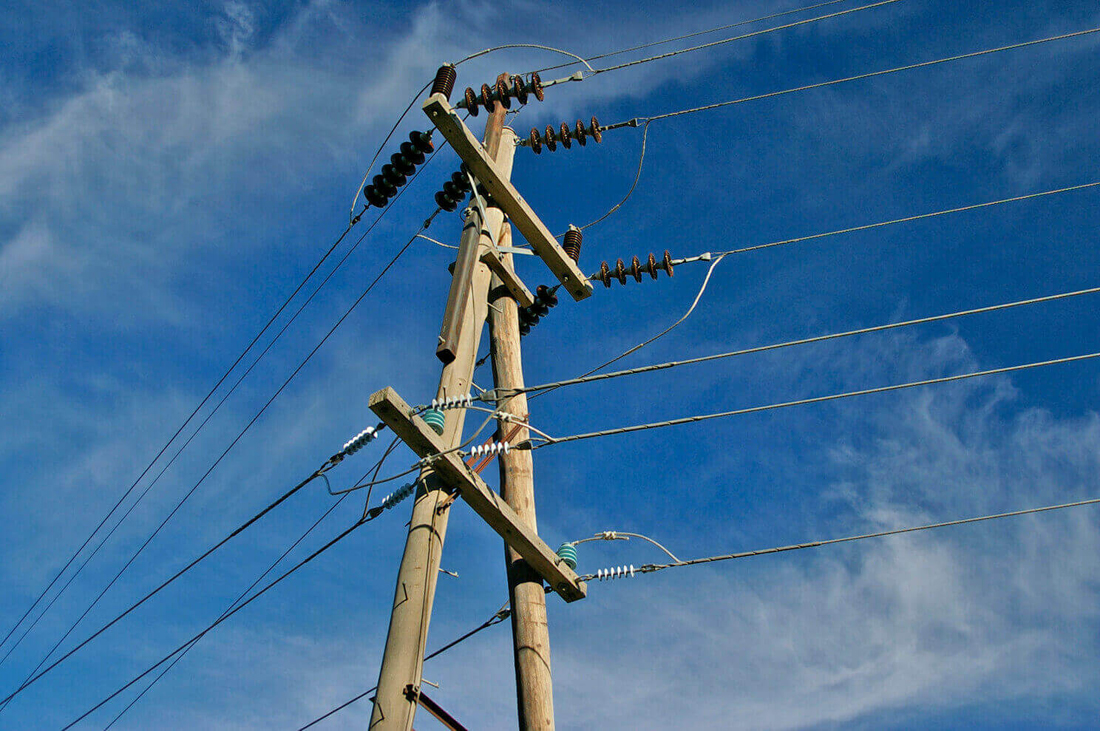
Electrical insulators play a crucial role in power transmission and distribution systems. They support and separate conductors, ensuring that the electric field and current remain confined within the conductors. They also help maintain the integrity of the wiring and prevent short circuits or leakage currents that may cause equipment damage or pose safety risks.
Several factors should be considered when selecting an electrical insulator for a specific application, including the operating voltage, environmental conditions, and mechanical stresses. The non-conductive material should possess a high dielectric constant, good resistance to temperature changes, and adequate mechanical strength. Additionally, it should resist environmental factors such as moisture, pollution, and UV radiation.
Various Types